
If nitrite ions do indeed contain a single and a double bond, we would expect for the two bond lengths to be different. The electrons involved in the N–O double bond, however, are in different positions: You may have noticed that the nitrite anion in can have two possible structures with the atoms in the same positions. Also, it places the least electronegative atom in the center, and the negative charge on the more electronegative element (Guideline 4). However, the first arrangement of atoms is preferred because it has the lowest number of atoms with nonzero formal charges (Guideline 2). Note that the sum of the formal charges in each case is equal to the charge of the ion (–1). Possible Lewis structures and the formal charges for each of the three possible structures for the thiocyanate ion are shown here: The formal charges present in each of these molecular structures can help us pick the most likely arrangement of atoms. We can draw three possibilities for the structure: carbon in the center and double bonds, carbon in the center with a single and triple bond, and oxygen in the center with double bonds:Ĭomparing the three formal charges, we can definitively identify the structure on the left as preferable because it has only formal charges of zero (Guideline 1).Īs another example, the thiocyanate ion, an ion formed from a carbon atom, a nitrogen atom, and a sulfur atom, could have three different molecular structures: CNS –, NCS –, or CSN –. We know from our previous discussion that the less electronegative atom typically occupies the central position, but formal charges allow us to understand why this occurs. To see how these guidelines apply, let us consider some possible structures for carbon dioxide, CO 2. When we must choose among several Lewis structures with similar distributions of formal charges, the structure with the negative formal charges on the more electronegative atoms is preferable.
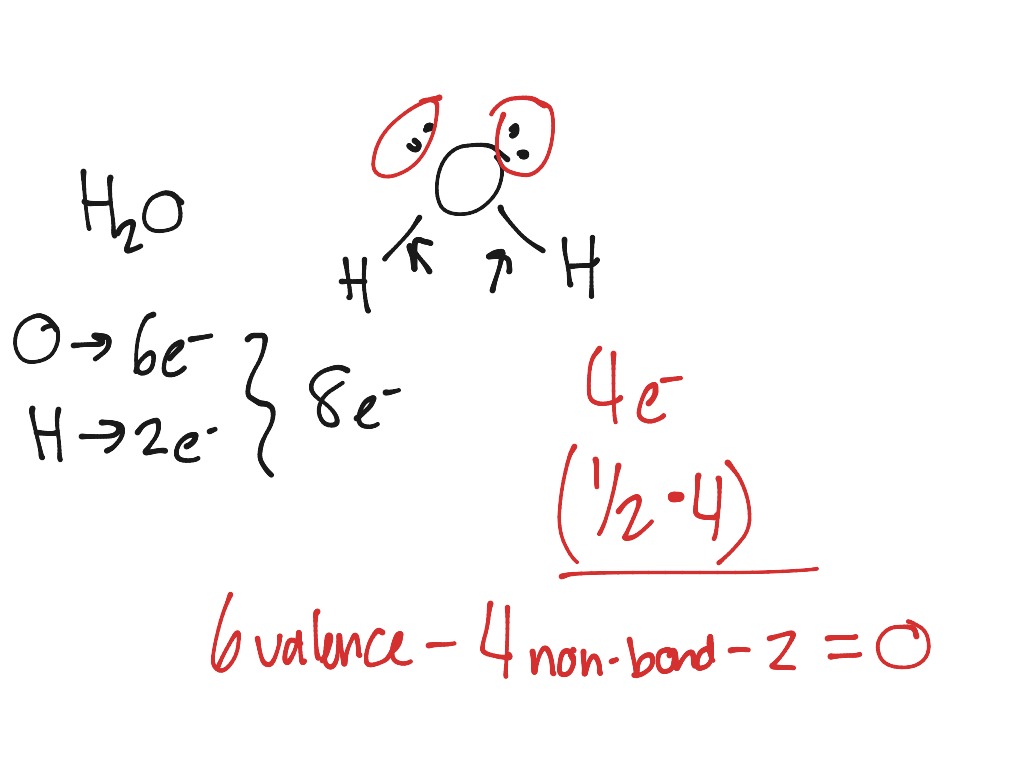
A molecular structure in which all formal charges are zero is preferable to one in which some formal charges are not zero.A few guidelines involving formal charge can be helpful in deciding which of the possible structures is most likely for a particular molecule or ion:

In many cases, following the steps for writing Lewis structures may lead to more than one possible molecular structure-different multiple bond and lone-pair electron placements or different arrangements of atoms, for instance. The arrangement of atoms in a molecule or ion is called its molecular structure. Using Formal Charge to Predict Molecular Structure


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
